In Uganda, wood furniture making was introduced in the early 1900s by the British Colonial
Government. During this time, majority of the natural high forests were intact with an abundance
of hard woods among which mahoganies (Khaya and Entandrophragma spp) and Mvule (Milicia
excelsa) were the timber species preferred by the furniture industry (Upton, 1996). By the late
60s and early 70s the industry had become well established producing products for both local
and regional markets. However, due to the political conflicts that occurred between 1977 and 1985, the industry experienced along recess period. During this conflict era,
skilled man power majority of who were of Indian origin left the country. Gradually, the wood
working machinery became obsolete and finally the industry was run down and all the factories
were vandalized.
In 1986, the civil war was ended and Law and order were restored in several parts of the country.
Ever since then, huge efforts have been made to salvage the economy under the national
Resistance Movement (NRM). Today, at a growth rate of 6.5% per year for the last ten years, the
economy of Uganda has steadily recovered (MFEPD, 2008). During this period, the construction
sector which is also the leading user of timber and furniture has experienced tremendous growth
(UBOS, 2006). At an averaged growth rate of 5 % per year, the furniture industry has
experienced a tremendous recovery over the last 10-15 years (Odokonyero, 2005).
The industry has also witnessed technological advancements as well. There has been a progressive shift from 8 old technology and traditional practices to modern wood working technology and craftsmanship
(Calvalho, 1999). At present, the furniture industry is perhaps the most vibrant sector within the wood industry in
Uganda. Mainly dominated by the small and micro scale producers
2004) the industry is expanding fast and making significant contribution to the economy.
According to UBOS report (2006), the furniture sub sector is employing 25% of the urban population especially the low income groups, youth, semi-literate and women. Although still a few, medium scale producers are also slowly taking the stage in furniture production in Uganda. A recent study by the Department of Forest Products Engineering of Makerere University (2011), reports up to 100 medium sized furniture producing firms producing
for the Kampala market. The most prominent ones include; Hwang Sung Furniture Company,
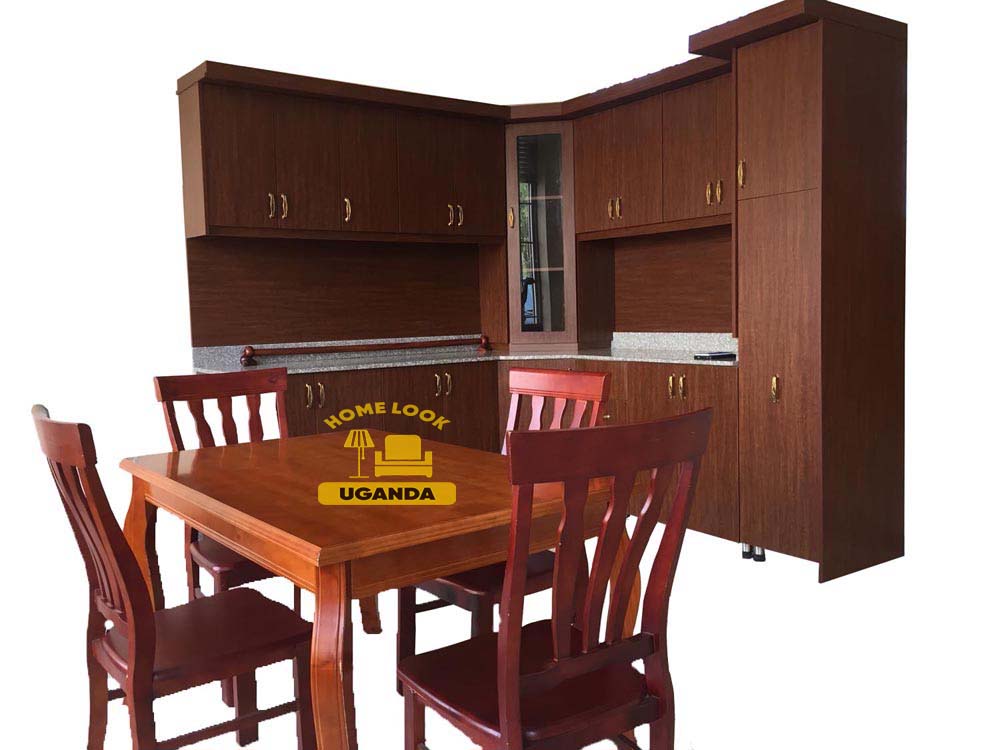
Erimu furniture company, Lotus Arts, Kaava Furniture Company, Biplous, Furniture Works , Home Look Uganda,
and Master Wood Furniture Company. These enterprises are based on high technology
machinery from Europe and Asia conferring high value addition and wood recovery.
Furniture Market and Distribution Channels in Kampala District
According to the Uganda Bureau of Statistic (UBOS) business report (2006), there are about 300
registered furniture businesses that sell office and household furniture in Uganda. The market is
mainly serving the domestic demand. Only 10% of furniture produced is exported mainly to
Rwanda, Kenya , Sudan and Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC). Furniture sales are by
majority made along streets (in show rooms) and through roadside displays in Kampala city and 9 its suburbs. The showrooms are mainly used by bigger furniture companies for high value products and less by small scale producers’ because of the high rental tariffs. Of recent, there has also been an increasing influx of household furniture imports into the Ugandan market. By the year 2003 alone, household furniture imports into the country had reached one million United States Dollars (Anon, 2003). The changing consumer preferences to high quality luxurious furniture are driving the shift in consumer preference to imported furniture especially among the middle and high income consumers. Although a hand full of reasons can exist to the question why urban consumers are preferring furniture imports, visual appeal (modern design and surface finish) is one of them.
This is because majority of the imports are mainly based on artificially 2engineered Wood and
produced from high technology systems. Compared to the locally produced furniture from
natural solid wood, engineered wood can be made to different light shades and surface finishes
that impact attractiveness to their furniture which may not be easily achieved by natural solid
wood. Moreover, majority of the small scale enterprises are still using low technology (hand
plane and saw) that may not permit complex value added designs.







Hey there! I simply would like to offer you a huge thumbs up for the excellent info you have got here on this post. I will be coming back to your website for more soon.